What is the True Range of an E-Bike?
The actual range of an Electric Bike is not always what is advertised
When we speak of range we are collectively referring to how far an electric bicycle will travel before the battery runs out of energy.
Range is determined primarily by 6 factors
-
The speed the bike is traveling
- The weight of the rider
-
The combined aerodynamic drag of the rider and bike
- How much the rider is pedaling
- The grade of the terrain
-
The efficiency of the motor drive system
-
The energy capacity of the battery (measured in Watt Hours or Wh)
If factors 1 to 5 are identical, then range is solely a function of the energy capacity of the battery and the efficiency of the motor drive system.
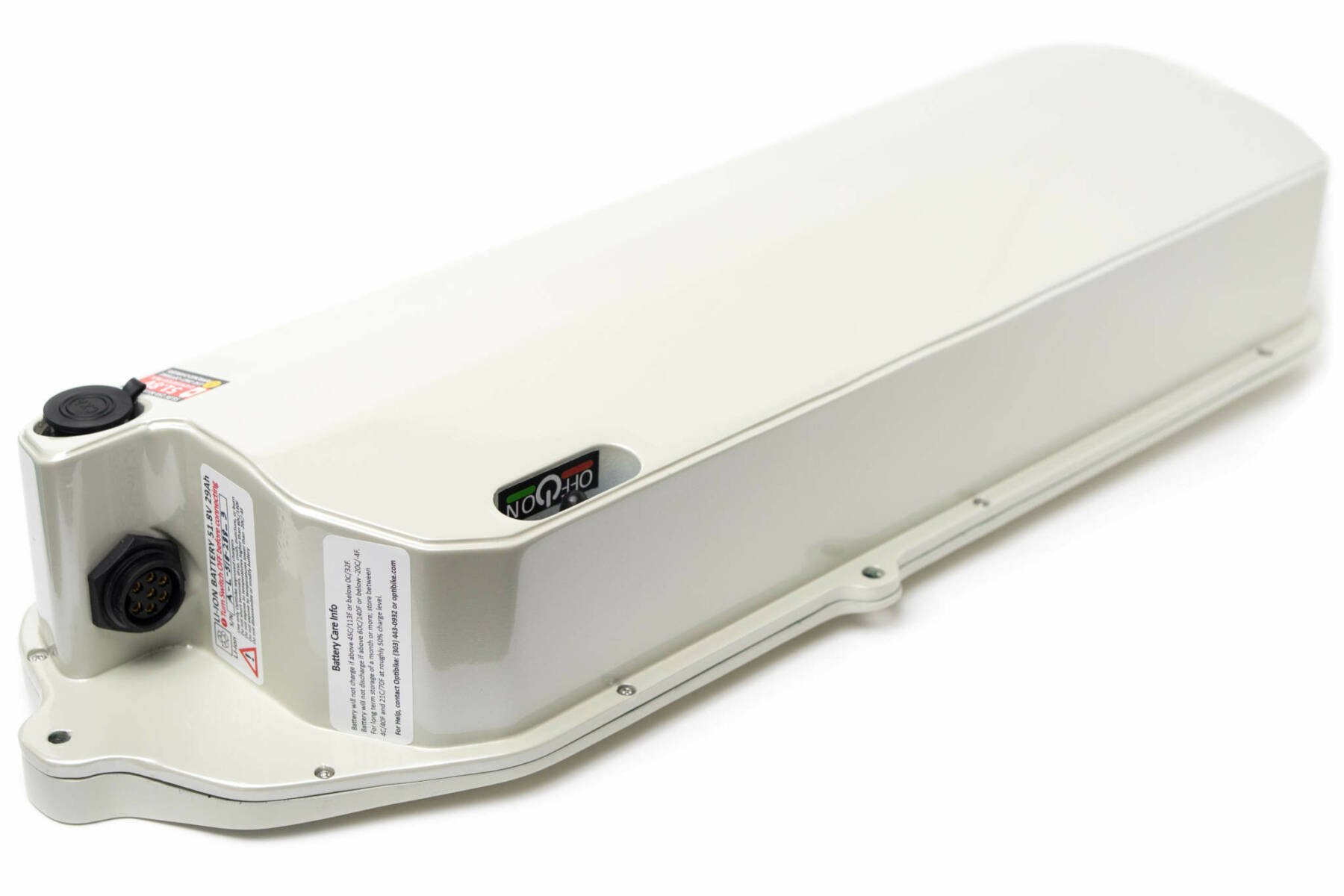
Battery Capacity
Energy capacity of a battery is measured in watt-hours (Wh) and is a product of volts times amp-hours. For example, a 37 volt battery with 10 amp-hours has an energy capacity of 370 watt-hours. This means the battery can put out roughly 370 watts for 1 hour.
Our Optibike R15C has a 1500 watt-hour battery, which means it can give you roughly 1500 watts of assist for 1 hour!
For long range touring purposes, Optibike pioneered the use of Lithium-Ion batteries, with the some of the largest battery capacities available in an electric bike.
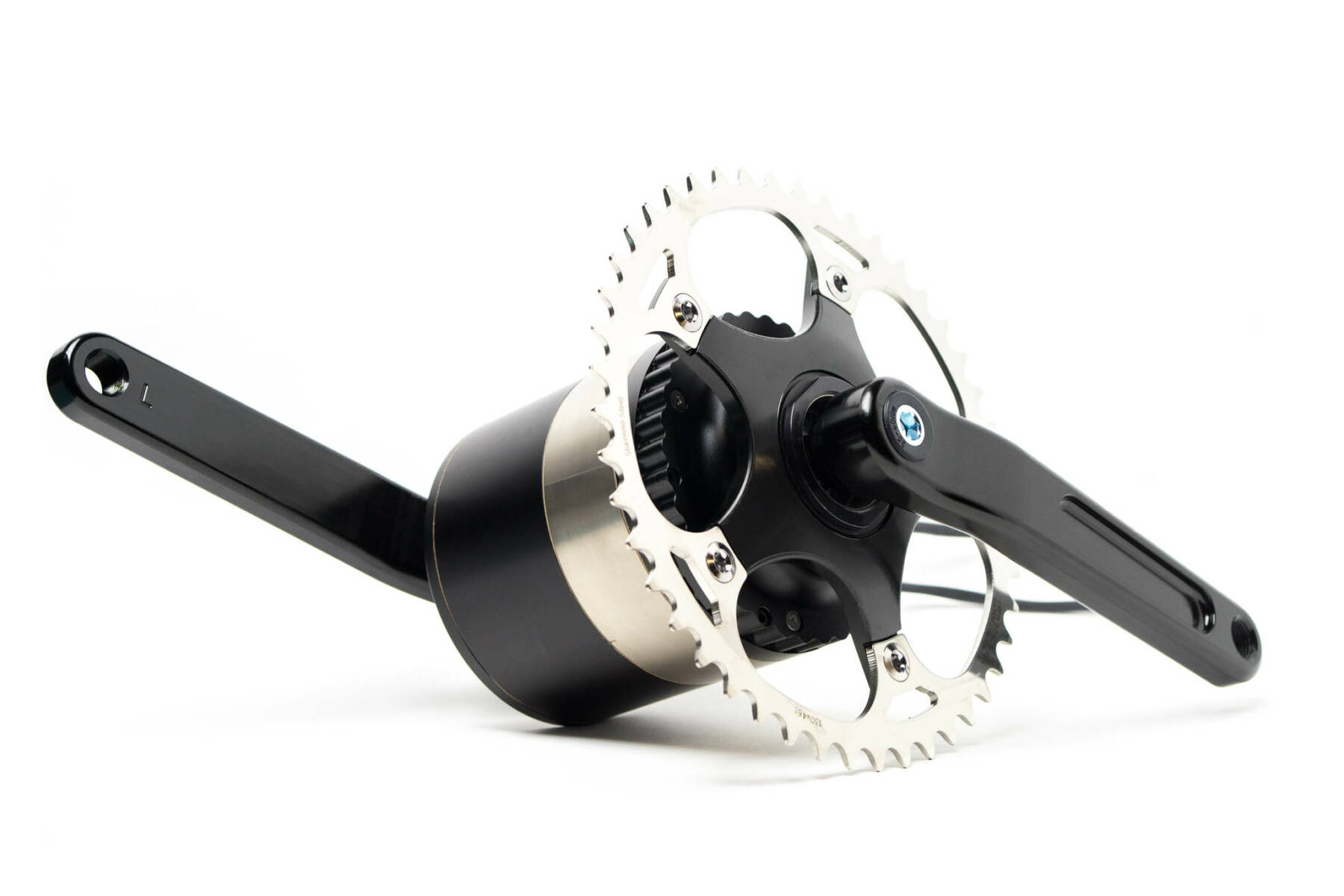
Motor Drive System
The efficiency of the motor drive system is also integral to electric bike range, all other factors considered equal.
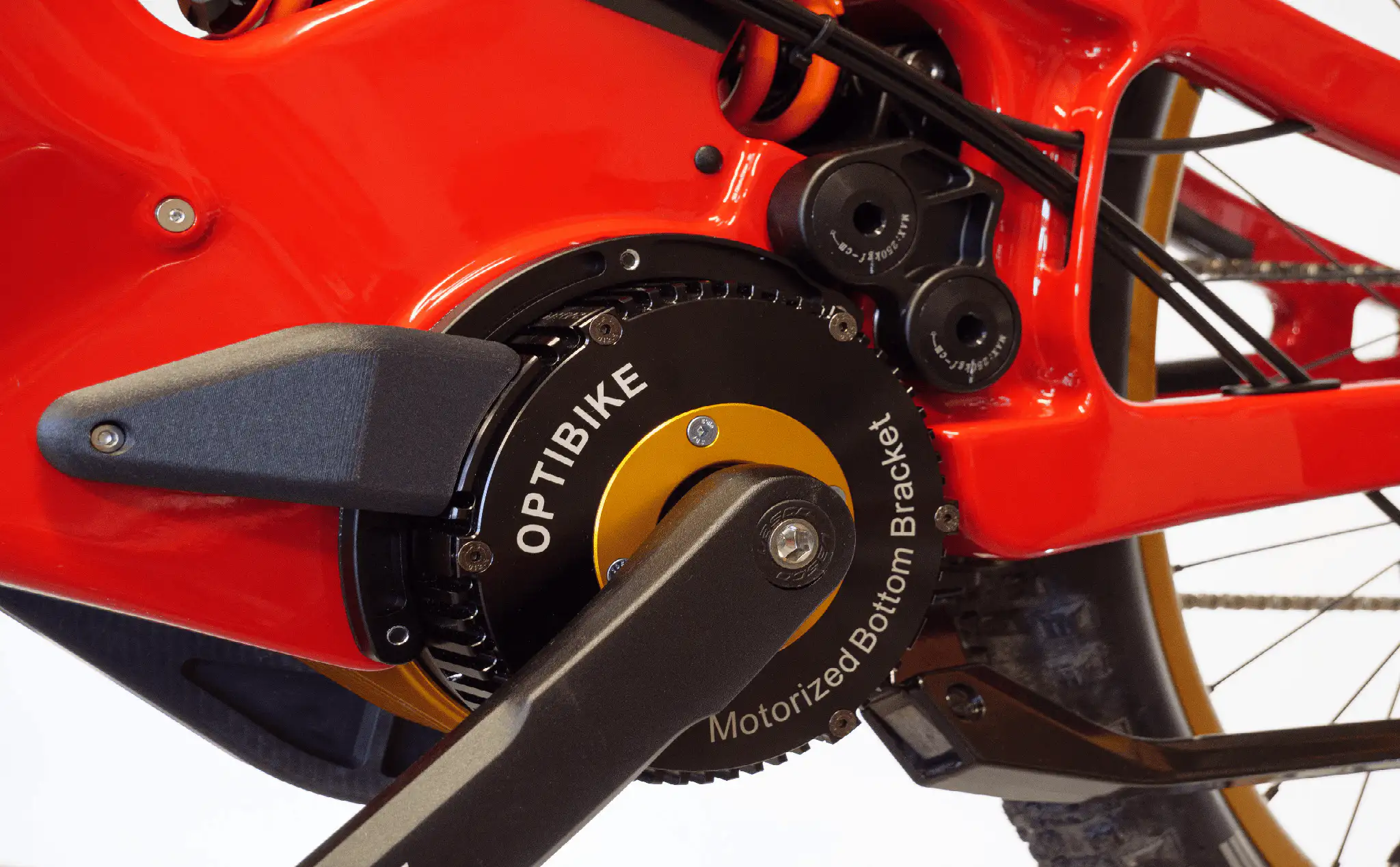
A motor drive system transfers energy from the battery to the wheels propelling you forward. Optibike revolutionized motor drives with the introduction of its patented Motorized Bottom Bracket (MBB) system, extending electric bike range.
The MBB has the highest power to volume ratio of any drive system, and is combined with a patented Derivative Power Control (DPC) system. DPC allows you to have both high acceleration and high efficiency, further extending your range.
(Video) Hub Motors vs Mid-Drive Motors
(Video) Battery Basics
Power & Torque – Why Torque Matters
On an electric bicycle, torque is the ability to rotate the rear wheel. Higher torque will create more acceleration and get you up steep hills easier. This means a bike with higher torque is easier to get going from a stop, or start on an incline.
More torque is also very useful off road; you can use it to climb over rough terrain or obstacles without the motor stalling and coming to a dead stop.
What is Torque?
The general definition of torque is the force on an arm at a distance from the center of rotation.
Torque = Force x Distance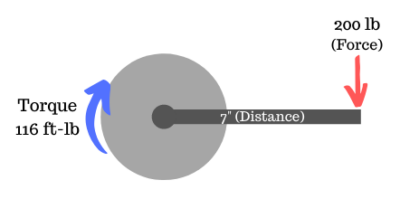 On a bicycle the rider pushes on the pedal to create Force, and the length of the crank arm is the Distance. Crank arms are typically 175 mm or 7 inches long. If the rider weighs 200 pounds and stands on the pedal, then the torque is 116 ft-lb as given by equation below:
On a bicycle the rider pushes on the pedal to create Force, and the length of the crank arm is the Distance. Crank arms are typically 175 mm or 7 inches long. If the rider weighs 200 pounds and stands on the pedal, then the torque is 116 ft-lb as given by equation below:
116 ft-lb = (200 pounds x 7 inches) / 12
Torque Units
With electric bikes you will see specs with torque listed in metric units (newton-meters | N-m) or US units (foot-pounds | ft-lb).
Here is a link to a useful calculator to covert between N-m and ft-lb
A common torque for lower powered e-bikes is 50 N-m,which can be converted to 36 ft-lb:
50 N-m = 36 ft-lb
For comparison our Optibike R15C has 190 N-m of torque:
190 N-m = 140 ft-lb
Electric Bicycle Glossary
Watts: A measure of power, 745.7 watts is equal to 1 horse power.
Power: More power gives you a higher top speed
RPM: Revolutions per minute
Torque: Torque = Force x Distance, torque is the ability of the motor or rider to rotate a wheel; higher torque gives faster acceleration
Voltage (V, volts): Voltage is electric potential, it moves current through a wire
Current (A, amps): Amps directly result in motor torque, as every motor has a torque constant (N-m per Amp)
Amp-hours (Ah): Capacity of a battery measured in amps for 1 hour
Watt-hours (Wh): Wh = V x Ah, total energy capacity of a battery
Pedalec Control: Electric bike where the power is controlled by the pedals
Throttle Control: Electric bike where the power is controlled with a throttle on the handlebar like a motorcycle













0 Comments